Key Concepts
The Role of an Agent
The core role of an Agent is to act on behalf of the user — autonomously assessing situations, executing necessary tasks, and providing intelligent solutions as a true partner.
Problem-Solving Ability: Understands user requests and independently selects the most appropriate execution path.
Context Retention: Utilizes memory to maintain the continuity of conversations and tasks.
Automation Expansion: Extends beyond simple dialogues to execute complex processes through the use of nodes and abilities.
Personalized Actions: Easily performs customized tasks by invoking user-designed abilities.
Structure and Operating Principle of an Agent
An Agent performs real tasks based on a Large Language Model (LLM).
Through a conversational interface, it enables human-like interaction and uses memory to continuously maintain context with the user.
This allows the agent to go beyond simple responses — demonstrating autonomous capabilities that include planning, execution, and feedback.
Agents in Agentria can operate independently or in combination with nodes and abilities to perform richer functions and more customized actions.
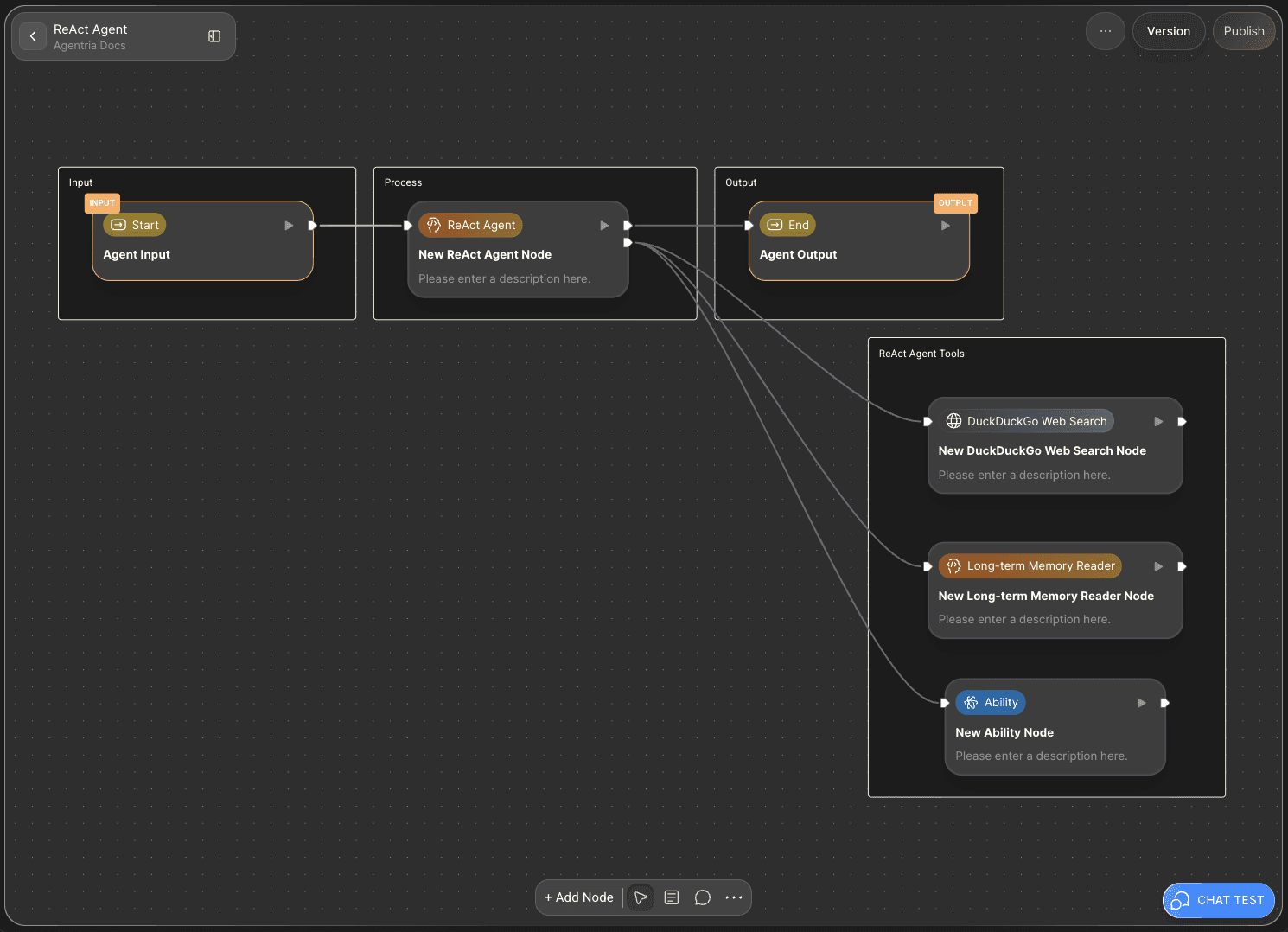
Components: AI Agents are built from nodes — the smallest functional units that perform specific operations.
Data Flow: Data is processed in a clear sequence of Input → Process → Output.
Input: Defines the data and parameters required for the AI Agent’s task.
Process: Internal nodes process the data, passing information through node connections. This is where the agent’s autonomous operation occurs.
Output: Returns the final result, providing the functional completeness of the AI Agent.